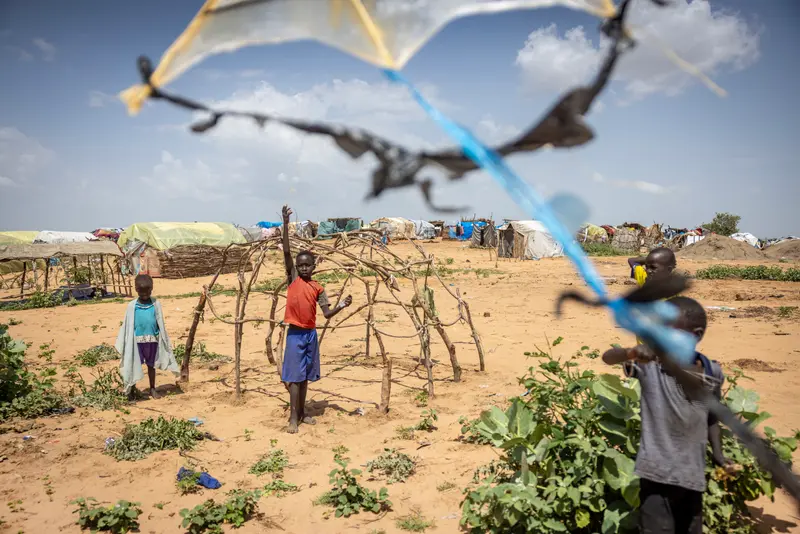
On Friday morning, the staffers at a half dozen U.S.-funded medical facilities in Sudan who care for severely malnourished children had a choice to make: Defy President Donald Trump’s order to immediately stop their operations or let up to 100 babies and toddlers die.
They chose the children.
In spite of the order, they will keep their facilities open for as long as they can, according to three people with direct knowledge of the situation. The people requested anonymity for fear that the administration might target their group for reprisals. Trump’s order also meant they would stop receiving new, previously approved funds to cover salaries, IV bags and other supplies. They said it’s a matter of days, not weeks, before they run out.
American-funded aid organizations around the globe, charged with providing lifesaving care for the most desperate and vulnerable populations imaginable, have for days been forced to completely halt their operations, turn away patients and lay off staff following a series of sudden stop-work demands from the Trump administration. Despite an announcement earlier this week ostensibly allowing lifesaving operations to continue, those earlier orders have not been rescinded.
Many groups doing such lifesaving work either don’t know the right way to request an exemption to the order, known as a waiver, or have no sense of where their request stands. They’ve received little information from the U.S. government, where, in recent days, humanitarian officials have been summarily ousted or prohibited from communicating with the aid organizations.
Trump’s rapid assault on the international aid system is quickly becoming the most consequential and far-reaching shift in U.S. humanitarian policy since the Marshall Plan to rebuild Europe after World War II, aid groups and government officials warned.
Among the programs that remain grounded as of Friday: emergency medical care for displaced Palestinians and Yemenis fleeing war, heat and electricity for Ukrainian refugees and HIV treatment and mpox surveillance in Africa.
What We’re Watching
During Donald Trump’s second presidency, ProPublica will focus on the areas most in need of scrutiny. Here are some of the issues our reporters will be watching — and how to get in touch with them securely.

Learn more about our reporting team. We will continue to share our areas of interest as the news develops.





If you don’t have a specific tip or story in mind, we could still use your help. Sign up to be a member of our federal worker source network to stay in touch.
We’re trying something new. Was it helpful?
Experts in and out of government have anxiously watched the fluid situation develop. “I’ve been an infectious disease doctor for 30 years, and I’ve never seen anything that scares me as much as this,” said Dr. Jennifer Furin, a Harvard Medical School physician who received a stop-work order for a program designing treatment plans for people with the most drug-resistant forms of tuberculosis. Infectious diseases do not know borders, she pointed out. “It’s terrifying.”
Trump and Secretary of State Marco Rubio first issued the freeze on aid operations last Friday, which included limited exemptions. “The pause on all foreign assistance means a complete halt,” a top adviser wrote in an internal memo to staff. (The order was separate from Trump’s now-seemingly rescinded moratorium on domestic U.S. grants.) Aid groups across the globe began receiving emails that instructed them to immediately stop working while the government conducted a 90-day review of their programs to make sure they aligned with the administration’s agenda.
Trump campaigned on an “America First” platform after unsuccessfully trying to slash the foreign assistance budget during his first term in office. The U.S. provides about $60 billion in nonmilitary humanitarian and development aid annually — less than 1% of the federal budget, but far more than any other country. The complex network of organizations who carry out the work is managed by the State Department and U.S. Agency for International Development.
Over the weekend, that system came to a standstill. There was widespread chaos and confusion as contractors scrambled to understand seemingly arbitrary orders from Washington and figure out how to get a waiver to continue working. By Tuesday evening, Trump and Rubio appeared to heed the international pressure and scale back the order by announcing that any “lifesaving” humanitarian efforts would be allowed to continue.
Aid groups that specialize in saving lives were relieved and thought their stop-work orders would be reversed just as swiftly as they had arrived.
But that hasn’t happened. Instead, more stop-work orders have been issued. As of Thursday, contractors worldwide were still grounded under the original orders and unable to secure waivers. Top Trump appointees arrested further funding and banned new projects for at least three months.
“We need to correct the impression that the waiver was self-executing by virtue of the announcement,” said Marcia Wong, the former deputy assistant administrator of USAID’s humanitarian assistance bureau.
Aid groups that had already received U.S. money were told they could not spend it or do any previously approved work. The contractors quoted in this article spoke on the condition of anonymity because they feared the administration might prolong their suspension or cancel their contracts completely.
As crucial days and hours pass, aid groups say Trump’s order has already caused irreparable harm. Often without cash reserves or endowments, many organizations depend on U.S. funding entirely and have been forced to lay off staff and cancel contracts with vendors. One CEO said he expects up to 3,000 aid workers to lose their jobs in Washington alone, according to the trade publication Devex. Some groups may have to shutter altogether because they can’t afford to float their overhead costs without knowing if or when they’d get reimbursed.
Critics say the past week has also undermined Trump’s own stated goals of American prosperity and security by opening a vacuum for international adversaries to fill, while putting millions at immediate and long-term risk.
“A chaotic, unexplained and abrupt pause with no guidance has left all our partners around the world high and dry and America looking like a severely unreliable actor to do business with,” a USAID official told ProPublica, adding that other countries will now have good reason to look to China or Russia for the help they’re no longer getting from the U.S. “There’s nothing that was left untouched.”
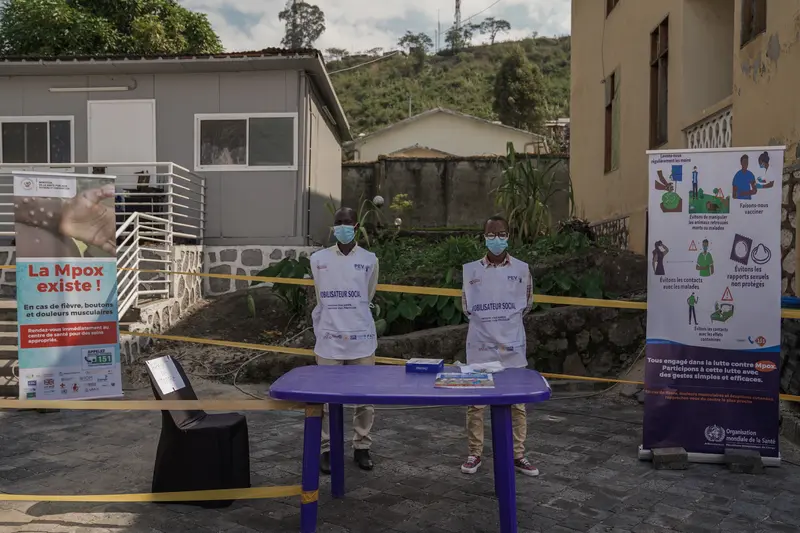

In response to a detailed list of questions for this article, the White House referred ProPublica to the State Department. The State Department said to direct all questions about USAID to the agency itself. USAID did not reply to our emails. Much of its communications staff was let go in the last week.
In a public statement Wednesday, the State Department defended the foreign aid freezes and said the government has issued dozens of exemption waivers in recent days.
“The previously announced 90-day pause and review of U.S. foreign aid is already paying dividends to our country and our people,” the statement said. “We are rooting out waste. We are blocking woke programs. And we are exposing activities that run contrary to our national interests. None of this would be possible if these programs remained on autopilot.”
The dire international situation has been exacerbated by upheaval in Washington. This week, the Trump administration furloughed 500 support staff contractors from USAID’s humanitarian assistance bureau, about 40% of the unit, and fired 400 more from the global health bureau. Those workers were told to stop working and “please head home.”
The remaining officials in Washington are now attempting to navigate a confounding waiver process and get lifesaving programs back online. Officials and diplomats told ProPublica that Trump’s new political appointees have not consulted USAID’s longtime humanitarian experts when crafting the new policies. As a result, career civil servants said they are struggling to understand the policy or how to carry it out.
During an internal meeting early in the week, one of USAID’s top Middle East officials told mission directors that the bar for aid groups to qualify for an exemption to Trump’s freeze was high, according to meeting notes. It took until Thursday for the directors to receive instructions for how to fill out a spreadsheet with the programs they think should qualify for a waiver and why, a government employee told ProPublica. “The waiver for humanitarian assistance has been a farce,” another USAID official said.
“Like a Russian nesting doll of fuck-ups,” said Jeremy Konyndyk, who ran some of USAID’s largest programs under Presidents Barack Obama and Joe Biden. “It’s just astonishing.”
Fear of retaliation is permeating the government’s foreign aid agencies, which have become some of Trump’s first targets in his campaign against diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives. Earlier this week, the administration pulled down photographs of children and families from the agency’s hallways.
Many are afraid of being punished or fired for doing their jobs. Officials in USAID’s humanitarian affairs bureau say they have been prohibited from even accepting calendar invites from aid organizations or setting up out-of-office email replies.
On Monday, USAID placed about 60 senior civil servants on administrative leave, citing unspecified attempts to “circumvent” the president’s agenda. The group received an email informing them of the decision without an explanation before they were locked out of the agency’s systems and banned from the building.
“We’re civil servants,” one of the officials said. “I should have been given notice, due process. Instead there was an agencywide notice accusing people of subverting the president’s executive orders.”
Then, on Thursday, the agency’s labor relations director told the group that he was withdrawing the agency’s decision because he found no evidence of misconduct, according to emails obtained by ProPublica.
Hours later, the director was put on administrative leave himself. “The agency’s front office and DOGE instructed me to violate the due process of our employees by issuing immediate termination notices,” he wrote to colleagues, referring to Trump’s Department of Government Efficiency run by Elon Musk. (Musk did not respond to a request for comment.)
Later that night, the original 60 officials were placed back on leave again.

Diplomats have long lauded American humanitarian efforts overseas because they help build crucial alliances around the world with relatively little cost.
When he created USAID in 1961, President John F. Kennedy called it a historic opportunity to improve the developing world so that countries don’t fall into economic collapse. That, he told Congress, “would be disastrous to our national security, harmful to our comparative prosperity and offensive to our conscience.”
USAID is responsible for the most successful international health program of the 21st century. The President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, created in 2003 by President George W. Bush to combat HIV globally, has saved an estimated 26 million lives over the past 22 years. It currently helps supply HIV medicines to 20 million people, and it funds HIV testing and jobs for thousands of health care workers, mainly in Africa.
That all ground to a halt this week. Since receiving the U.S. government’s stop-work orders, contractors who manage the program say they have so far received little communication about what work they will be allowed to continue, or when. They are not allowed to hand out medicines already bought and sitting on shelves.
If the exemption waivers don’t come through, policy analysts and HIV advocates say the full 90-day suspension of those programs would have disastrous consequences. More than 222,000 people pick up HIV treatment every day through the program, according to an analysis by amFAR, a nonprofit dedicated to AIDS research and advocacy. As of Friday morning, those orders had not been lifted, according to three people with direct knowledge.
Up through last week, PEPFAR was providing HIV treatment to an estimated 680,000 pregnant women, the majority of whom are in Africa. A 90-day stoppage could lead to an estimated 136,000 babies acquiring HIV, according to the amfAR analysis. Since HIV testing services are also suspended, many of those could go undiagnosed.
The disarray has also reached warzones and foreign governments, risking disease outbreaks and straining international relationships forged over decades.
Government officials worried about contract personnel who were suddenly stranded in remote locations. In Syria, camp managers were told to abandon their site at al-Hawl refugee camp, which is also a prison for ISIS sympathizers. That left the refugees inside with nowhere to turn for basic supplies like food and gas.
In Mogadishu, Somalia, the State Department instructed security guards who were protecting an arms depot from insurgents to simply walk off the site, according to a company official. When the guards asked what would happen to the armory, their government contacts told them they didn’t have any answers. (Concerns about the armory were first reported by The Wall Street Journal.)
The contractors in Syria and Somalia have since been allowed to return to their sites.
An executive at a health care nonprofit told ProPublica he has not been so lucky. His group is still under the stop-work order and can’t fund medical operations in Gaza, where there is a fragile ceasefire deal between Hamas and Israel that depends in part on the free flow of humanitarian aid.
“People will die,” the executive said. “For organizations that rely solely or largely on U.S. government funding, this hurts. That may be part of the message. But there would be less drastic ways to send it.”
In response to criticism, the Trump administration has offered misinformation. During a press conference, Karoline Leavitt, the White House press secretary, touted the initiative’s success so far and said the government “found that there was about to be $50 million taxpayer dollars that went out the door to fund condoms in Gaza.” Trump later went further, saying Hamas fighters were using the condoms to make explosives.
They didn’t name the contractor, but the State Department later cited $100 million in canceled aid packages slated for the International Medical Corps.
IMC said in a response that no U.S. government funding was used for condoms or any other family-planning services. The organization has treated more than 33,000 Palestinians a month, according to the statement. It also operates one of the only centers in Gaza for severely malnourished children.
“If the stop-work order remains in place,” IMC said, “we will be unable to sustain these activities beyond the next week or so.”
There are also new outbreaks of Ebola in Uganda’s capital and of the disease’s cousin, the Marburg virus, in Tanzania. The U.S. has long been a key funder of biosecurity measures internationally, including at high-security labs. That funding is now on hold.
In Ukraine, groups that provide vital humanitarian aid for civilians and soldiers fighting Russia have been told to stand down without any meaningful updates in days, according to three officials familiar with the situation. The halted services include first responders, fuel for hospitals and evacuation routes for refugees fleeing the front lines.
“These are people who have been living in a war zone for three years this month,” the head of one of the organizations said, adding that they may have to lay off 20% of its staff. “And we are taking away these very basic services that they need to survive.”

A contractor for the U.S. in Yemen said her entire team had been told to stop their work last weekend, which ProPublica corroborated with contemporaneous emails. “One of my tasks was summarizing how many people had been directly saved by our health programs every week,” she said. “It was usually 80 to 100.”
Their stop-work order has not been lifted. It will be a week on Sunday.










